title: javascript 数据结构与算法–学习笔记
对栈的理解是,栈是一段存储空间,供系统或者操作系统使用,对程序员来说一般是不可见的,除非从一开始由程序员自己通过汇编等自己构建栈,栈会由系统管理单元自己申请释放。栈是从高地址向低地址生长的,既栈底在高地址,栈顶低地址。
2.堆 通俗意义上这样理解堆,堆是一段非常大的内存空间,供不同的程序员从其中取出一段供自己使用,使用之后要由程序员自己释放,如果不释放的话,这部分存储空间将不能被其他程序使用。堆的存储空间是不连续的,因为会因为不同时间,不同大小的堆空间的申请导致其不连续性。堆的生长是从低地址向高地址增长的。
3.基本算法 3.1 冒泡算法: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 var arr = [2, 1, 4, 3]; for (var i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { for (var j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) { if(arr[i]>arr[j]){ var x = arr[j]; //重点就是这个中间值做转换 arr[j] = arr[i]; arr[i] = x; } } } console.log(arr)
3.2 快排算法: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 var arr = [7, 5, 7, 2, 1, 6, 9, 7, 5, 6]; var i = 0, j = arr.length - 1; function sort(arr) { var bridge = arr[i]; if (arr[i] >= arr[j]) { arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = bridge; j--; if (j > i) { sort(arr); } else { i++; if(i<=arr.length-2){ j = arr.length - 1; sort(arr); }else{ return arr; } } } else { j--; if (j > i) { sort(arr); }else{ i++; if(i<=arr.length-2){ j = arr.length - 1; sort(arr); }else{ return arr; } } } return arr; } // ★简化后 // function sort(arr) { // var bridge = arr[i]; // if (arr[i] >= arr[j]) { // arr[i] = arr[j]; // arr[j] = bridge; // } // j--; // if (j > i) { // sort(arr); // } else { // i++; // if (i <= arr.length - 2) { // j = arr.length - 1; // sort(arr); // } // } // return arr; // } var newArr = sort(arr); console.log(newArr)
1.javascript 简介 1.2.4 相等操作符 toPrimitive 方法是内部方法,对不同类型返回的结果是,如果对象的 valueOf 方法的结果是原始值,返回原始值。如果对象的 toString 方法返回原始值,就返回这个值,其他情况返回一个错误
1.3.1 条件语句 对于 switch 语句来说,case和break关键字非常重要 。
1.4 函数 函数只接受一个参数的话,如果传入两个参数,会忽略掉第二个参数。
1.5 面向对象编程 原型方法:可以节约内存和降低实例化的开销
2. 数组 数组缺点:(在大多数语言中)数组的大小是固定的,从数组的起点或中间插入或移除项的成本很高,因为需要移动元素
2.4 二维和多维数组 嵌套循环
2.5.3 搜索和排序 sort方法对数组做排序,是把元素默认成字符串对应的 ASCII 值进行比较的
3. 栈 遵从后进先出 (LIFO)原则的有序集合。栈的方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 function Stack() { var items = []; this.push = function(element){ items.push(element); }; this.pop = function(){ return items.pop(); }; this.peek = function(){ return items[items.length-1]; }; this.isEmpty = function(){ return items.length == 0; }; this.size = function(){ return items.length; }; this.clear = function(){ items = []; }; this.print = function(){ console.log(items.toString()); }; this.toString = function(){ return items.toString(); }; }
3.2 十进制转二进制 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 function divideBy2(decNumber){ var remStack = new Stack(), rem, binaryString = ''; while (decNumber > 0){ rem = Math.floor(decNumber % 2); remStack.push(rem); decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / 2); } while (!remStack.isEmpty()){ binaryString += remStack.pop().toString(); } return binaryString; } console.log(divideBy2(233)); console.log(divideBy2(10)); console.log(divideBy2(1000));
4. 队列 遵从(FIFO)先进先出原则的一组有序的项。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 function Queue() { var items = []; this.enqueue = function(element){ items.push(element); }; this.dequeue = function(){ return items.shift(); }; this.front = function(){ return items[0]; }; this.isEmpty = function(){ return items.length == 0; }; this.clear = function(){ items = []; }; this.size = function(){ return items.length; }; this.print = function(){ console.log(items.toString()); }; }
4.2 优先队列 例子:急诊科,医生会根据病情优先病情严重的人先看
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 function PriorityQueue() { var items = []; function QueueElement (element, priority){ this.element = element; this.priority = priority; } this.enqueue = function(element, priority){ var queueElement = new QueueElement(element, priority); if (this.isEmpty()){ items.push(queueElement); } else { var added = false; for (var i=0; i<items.length; i++){ if (queueElement.priority < items[i].priority){ items.splice(i,0,queueElement); //数组的插入方法 added = true; break; } } if (!added){ items.push(queueElement); } } }; this.dequeue = function(){ return items.shift(); }; this.front = function(){ return items[0]; }; this.isEmpty = function(){ return items.length == 0; }; this.size = function(){ return items.length; }; this. print = function(){ for (var i=0; i<items.length; i++){ console.log(items[i].element + ' - ' + items[i].priority); } }; } var priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(); priorityQueue.enqueue("John", 2); priorityQueue.enqueue("Jack", 1); priorityQueue.enqueue("Camila", 1); priorityQueue.enqueue("Maxwell", 2); priorityQueue.enqueue("Ana", 3); priorityQueue.print();
4.3 循环列队–击鼓传花 某一时刻传花停止,这个时候花在谁手里,谁就退出圆圈结束游戏。重复这个过程,直到只剩一个孩子(胜者) 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function hotPotato (nameList, num){ var queue = new Queue(); for (var i=0; i<nameList.length; i++){ queue.enqueue(nameList[i]); } var eliminated = ''; while (queue.size() > 1){ for (var i=0; i<num; i++){ queue.enqueue(queue.dequeue()); //循环起来,传num次 } eliminated = queue.dequeue(); //传了num后的最后一个人就是被淘汰的人 console.log(eliminated + ' was eliminated from the Hot Potato game.'); } return queue.dequeue(); } var names = ['John','Jack','Camila','Ingrid','Carl']; var winner = hotPotato(names, 7); console.log('The winner is: ' + winner);
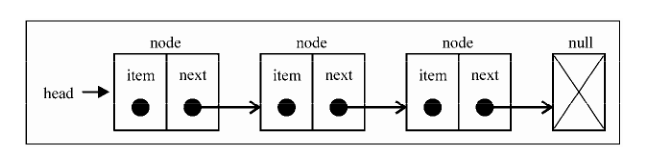
5. 链表 数组缺点:(在大多数语言中)数组的大小是固定的,从数组的起点或中间插入或移除项的成本很高,因为需要移动元素
链表方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 //current 是不存在的会被node替换掉 function LinkedList() { var Node = function(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; }; var length = 0; var head = null; this.append = function(element){ var node = new Node(element), current; if (head === null){ //first node on list head = node; } else { current = head; //loop the list until find last item while(current.next){ current = current.next; } //get last item and assign next to added item to make the link current.next = node; } length++; //update size of list }; this.insert = function(position, element){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= length){ var node = new Node(element), current = head, previous, index = 0; if (position === 0){ //add on first position node.next = current; head = node; } else { while (index++ < position){ previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; } length++; //update size of list return true; } else { return false; } }; this.removeAt = function(position){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < length){ var current = head, previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0){ head = current.next; } else { while (index++ < position){ previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; } length--; return current.element; } else { return null; } }; this.remove = function(element){ var index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); }; this.indexOf = function(element){ var current = head, index = 0; while (current) { if (element === current.element) { return index; } index++; current = current.next; } return -1; }; this.isEmpty = function() { return length === 0; }; this.size = function() { return length; }; this.getHead = function(){ return head; }; this.toString = function(){ var current = head, string = ''; while (current) { string = current.element; current = current.next; } return string; }; this.print = function(){ console.log(this.toString()); }; }
5.2 双向链表 在单向链表中,如果迭代列表时错过了要找的元素,就需要回到 列表起点,重新开始迭代。这是双向链表的一个优点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 function DoublyLinkedList() { var Node = function(element){ this.element = element; this.next = null; this.prev = null; //NEW }; var length = 0; var head = null; var tail = null; //NEW this.append = function(element){ var node = new Node(element), current; if (head === null){ //first node on list head = node; tail = node; //NEW } else { //attach to the tail node //NEW tail.next = node; node.prev = tail; tail = node; } length++; //update size of list }; this.insert = function(position, element){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position >= 0 && position <= length){ var node = new Node(element), current = head, previous, index = 0; if (position === 0){ //add on first position if (!head){ //NEW head = node; tail = node; } else { node.next = current; current.prev = node; //NEW {1} head = node; } } else if (position === length) { //last item //NEW current = tail; // {2} current.next = node; node.prev = current; tail = node; } else { while (index++ < position){ //{3} previous = current; current = current.next; } node.next = current; previous.next = node; current.prev = node; //NEW node.prev = previous; //NEW } length++; //update size of list return true; } else { return false; } }; this.removeAt = function(position){ //check for out-of-bounds values if (position > -1 && position < length){ var current = head, previous, index = 0; //removing first item if (position === 0){ head = current.next; // {1} //if there is only one item, then we update tail as well //NEW if (length === 1){ // {2} tail = null; } else { head.prev = null; // {3} } } else if (position === length-1){ //last item //NEW current = tail; // {4} tail = current.prev; tail.next = null; } else { while (index++ < position){ // {5} previous = current; current = current.next; } //link previous with current's next - skip it to remove previous.next = current.next; // {6} current.next.prev = previous; //NEW } length--; return current.element; } else { return null; } }; this.remove = function(element){ var index = this.indexOf(element); return this.removeAt(index); }; this.indexOf = function(element){ var current = head, index = -1; //check first item if (element == current.element){ return 0; } index++; //check in the middle of the list while(current.next){ if (element == current.element){ return index; } current = current.next; index++; } //check last item if (element == current.element){ return index; } return -1; }; this.isEmpty = function() { return length === 0; }; this. size = function() { return length; }; this.toString = function(){ var current = head, s = current ? current.element : ''; while(current && current.next){ current = current.next; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s; }; this.inverseToString = function() { var current = tail, s = current ? current.element : ''; while(current && current.prev){ current = current.prev; s += ', ' + current.element; } return s; }; this.print = function(){ console.log(this.toString()); }; this.printInverse = function(){ console.log(this.inverseToString()); }; this.getHead = function(){ return head; }; this.getTail = function(){ return tail; } }
5.3 循环列表 6. 集合(Set 类) [值,值]–其实就是 key=value 集合:由一组无序且唯一(即不重复)的项组成的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 function Set() { var items = {}; this.add = function(value){ if (!this.has(value)){ items[value] = value; return true; } return false; }; this.remove = function(value){ if (this.has(value)){ delete items[value]; return true; } return false; }; this.has = function(value){ return items.hasOwnProperty(value); //return value in items; }; this.clear = function(){ items = {}; }; /** * Modern browsers function * IE9+, FF4+, Chrome5+, Opera12+, Safari5+ * @returns {Number} */ this.size = function(){ return Object.keys(items).length; }; /** * cross browser compatibility - legacy browsers * for modern browsers use size function * @returns {number} */ this.sizeLegacy = function(){ var count = 0; for(var prop in items) { if(items.hasOwnProperty(prop)) ++count; } return count; }; /** * Modern browsers function * IE9+, FF4+, Chrome5+, Opera12+, Safari5+ * @returns {Array} */ this.values = function(){ return Object.keys(items); }; this.valuesLegacy = function(){ var keys = []; for(var key in items){ keys.push(key); } return keys; }; this.getItems = function(){ return items; }; this.union = function(otherSet){ var unionSet = new Set(); //{1} var values = this.values(); //{2} for (var i=0; i<values.length; i++){ unionSet.add(values[i]); } values = otherSet.values(); //{3} for (var i=0; i<values.length; i++){ unionSet.add(values[i]); } return unionSet; }; this.intersection = function(otherSet){ var intersectionSet = new Set(); //{1} var values = this.values(); for (var i=0; i<values.length; i++){ //{2} if (otherSet.has(values[i])){ //{3} intersectionSet.add(values[i]); //{4} } } return intersectionSet; }; this.difference = function(otherSet){ var differenceSet = new Set(); //{1} var values = this.values(); for (var i=0; i<values.length; i++){ //{2} if (!otherSet.has(values[i])){ //{3} differenceSet.add(values[i]); //{4} } } return differenceSet; }; this.subset = function(otherSet){ if (this.size() > otherSet.size()){ //{1} return false; } else { var values = this.values(); for (var i=0; i<values.length; i++){ //{2} if (!otherSet.has(values[i])){ //{3} return false; //{4} } } return true; } }; }
7. 字典(Map) [键,值] 和 散列表[{},{}] 字典也称映射。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 function Dictionary(){ var items = {}; this.set = function(key, value){ items[key] = value; //{1} }; this.remove = function(key){ if (this.has(key)){ delete items[key]; return true; } return false; }; this.has = function(key){ return items.hasOwnProperty(key); //return value in items; }; this.get = function(key) { return this.has(key) ? items[key] : undefined; }; this.clear = function(){ items = {}; }; this.size = function(){ return Object.keys(items).length; }; this.keys = function(){ return Object.keys(items); }; this.values = function(){ var values = []; for (var k in items) { if (this.has(k)) { values.push(items[k]); } } return values; }; this.each = function(fn) { for (var k in items) { if (this.has(k)) { fn(k, items[k]); } } }; this.getItems = function(){ return items; } }
7.2 散列表–也叫 HashTable 或 HashMap 前边的数据结构在获取值的时候,需要遍历整个 数据结构来找到它。如果使用散列函数,就知道值的具体位置,因此能够快速检索到该值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 function HashTable() { var table = []; var loseloseHashCode = function (key) { var hash = 0; for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) { hash += key.charCodeAt(i); } return hash % 37; }; var djb2HashCode = function (key) { var hash = 5381; for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) { hash = hash * 33 + key.charCodeAt(i); } return hash % 1013; }; var hashCode = function (key) { return loseloseHashCode(key); }; this.put = function (key, value) { var position = hashCode(key); console.log(position + ' - ' + key); table[position] = value; }; this.get = function (key) { return table[hashCode(key)]; }; this.remove = function(key){ table[hashCode(key)] = undefined; }; this.print = function () { for (var i = 0; i < table.length; ++i) { if (table[i] !== undefined) { console.log(i + ": " + table[i]); } } }; }
7.2.3 散列表和散列集合 散列表:[{},{}]
7.2.4 处理散列表中的冲突 如果发生冲突:后添加的会覆盖之前添加的值
7.2.4.1 分离链接 结构为:[{key:[这里是发生冲突的项]},{key:[这里是发生冲突的项]}]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 function HashTableSeparateChaining(){ var table = []; var ValuePair = function(key, value){ this.key = key; this.value = value; this.toString = function() { return '[' + this.key + ' - ' + this.value + ']'; } }; var loseloseHashCode = function (key) { var hash = 0; for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) { hash += key.charCodeAt(i); } return hash % 37; }; var hashCode = function(key){ return loseloseHashCode(key); }; this.put = function(key, value){ var position = hashCode(key); console.log(position + ' - ' + key); if (table[position] == undefined) { table[position] = new LinkedList(); } table[position].append(new ValuePair(key, value)); }; this.get = function(key) { var position = hashCode(key); if (table[position] !== undefined && !table[position].isEmpty()){ //iterate linked list to find key/value var current = table[position].getHead(); while(current.next){ if (current.element.key === key){ return current.element.value; } current = current.next; } //check in case first or last element if (current.element.key === key){ return current.element.value; } } return undefined; }; this.remove = function(key){ var position = hashCode(key); if (table[position] !== undefined){ //iterate linked list to find key/value var current = table[position].getHead(); while(current.next){ if (current.element.key === key){ table[position].remove(current.element); if (table[position].isEmpty()){ table[position] = undefined; } return true; } current = current.next; } //check in case first or last element if (current.element.key === key){ table[position].remove(current.element); if (table[position].isEmpty()){ table[position] = undefined; } return true; } } return false; }; this.print = function() { for (var i = 0; i < table.length; ++i) { if (table[i] !== undefined) { console.log(table[i].toString()); } } }; }
7.2.4.2 线性探查 其实就是通过移位的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 function HashLinearProbing(){ var table = []; var ValuePair = function(key, value){ this.key = key; this.value = value; this.toString = function() { return '[' + this.key + ' - ' + this.value + ']'; } }; var loseloseHashCode = function (key) { var hash = 0; for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) { hash += key.charCodeAt(i); } return hash % 37; }; var hashCode = function(key){ return loseloseHashCode(key); }; this.put = function(key, value){ var position = hashCode(key); console.log(position + ' - ' + key); if (table[position] == undefined) { table[position] = new ValuePair(key, value); } else { var index = ++position; while (table[index] != undefined){ index++; } table[index] = new ValuePair(key, value); } }; this.get = function(key) { var position = hashCode(key); if (table[position] !== undefined){ if (table[position].key === key) { return table[position].value; } else { var index = ++position; while (table[index] === undefined || table[index].key !== key){ index++; } if (table[index].key === key) { return table[index].value; } } } return undefined; }; this.remove = function(key){ var position = hashCode(key); if (table[position] !== undefined){ if (table[position].key === key) { table[position] = undefined; } else { var index = ++position; while (table[index] === undefined || table[index].key !== key){ index++; } if (table[index].key === key) { table[index] = undefined; } } } }; this.print = function() { for (var i = 0; i < table.length; ++i) { if (table[i] !== undefined) { console.log(i + ' -> ' + table[i].toString()); } } }; }
7.2.5 创建更好的散列函数 之前的散列函数造成的冲突太多了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var djb2HashCode = function (key) { var hash = 5381; //{1} for (var i = 0; i < key.length; i++) { //{2} hash = hash * 33 + key.charCodeAt(i); //{3} } return hash % 1013; //{4} };
8. 树 非顺序数据结构,对于存储需要快速查找数据 非常有用
8.2 二叉树和二叉搜索树 二叉搜索树(BST):左侧节点存储小 的值,在右侧节点存储大 (或者等于)的值。
方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 function BinarySearchTree() { var Node = function(key){ this.key = key; this.left = null; this.right = null; }; var root = null; this.insert = function(key){ var newNode = new Node(key); //special case - first element if (root === null){ root = newNode; } else { insertNode(root,newNode); } }; var insertNode = function(node, newNode){ if (newNode.key < node.key){ if (node.left === null){ node.left = newNode; } else { insertNode(node.left, newNode); } } else { if (node.right === null){ node.right = newNode; } else { insertNode(node.right, newNode); } } }; this.getRoot = function(){ return root; }; this.search = function(key){ return searchNode(root, key); }; var searchNode = function(node, key){ if (node === null){ return false; } if (key < node.key){ return searchNode(node.left, key); } else if (key > node.key){ return searchNode(node.right, key); } else { //element is equal to node.item return true; } }; //中序遍历 this.inOrderTraverse = function(callback){ inOrderTraverseNode(root, callback); }; var inOrderTraverseNode = function (node, callback) { if (node !== null) { //停止递归继续执行的条件 inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback); callback(node.key); inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback); } }; //先序遍历 this.preOrderTraverse = function(callback){ preOrderTraverseNode(root, callback); }; var preOrderTraverseNode = function (node, callback) { if (node !== null) { callback(node.key); preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback); preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback); } }; //后续遍历 this.postOrderTraverse = function(callback){ postOrderTraverseNode(root, callback); }; var postOrderTraverseNode = function (node, callback) { if (node !== null) { postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback); postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback); callback(node.key); } }; this.min = function() { return minNode(root); }; var minNode = function (node) { if (node){ while (node && node.left !== null) { node = node.left; } return node.key; } return null; }; this.max = function() { return maxNode(root); }; var maxNode = function (node) { if (node){ while (node && node.right !== null) { node = node.right; } return node.key; } return null; }; this.remove = function(element){ root = removeNode(root, element); }; var findMinNode = function(node){ while (node && node.left !== null) { node = node.left; } return node; }; var removeNode = function(node, element){ if (node === null){ return null; } if (element < node.key){ node.left = removeNode(node.left, element); return node; } else if (element > node.key){ node.right = removeNode(node.right, element); return node; } else { //element is equal to node.item //handle 3 special conditions //1 - a leaf node //2 - a node with only 1 child //3 - a node with 2 children //case 1 if (node.left === null && node.right === null){ node = null; return node; } //case 2 if (node.left === null){ node = node.right; return node; } else if (node.right === null){ node = node.left; return node; } //case 3 var aux = findMinNode(node.right); node.key = aux.key; node.right = removeNode(node.right, aux.key); return node; } }; }
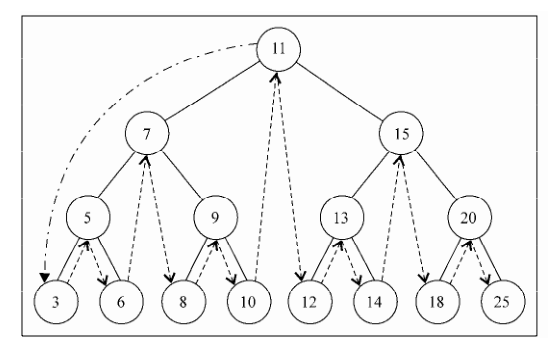
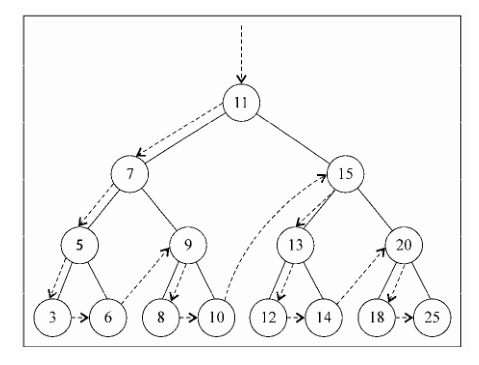
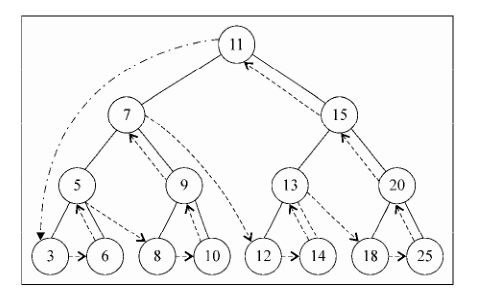
8.3 树的遍历 8.3.1 中序遍历 从最小到最大的顺序访问所有节点。
8.3.2 先序遍历 先序遍历是以优先于后代节点的顺序访问每个节点的。
8.3.3 后续遍历 后序遍历则是先访问节点的后代节点,再访问节点本身。
8.4 搜索树中的值 8.4.1 搜索最小值和最大值 最左边是最小值
8.4.2 搜索一个特定的值 当key<node.key 和key>node.key都不成立的时候,就是等于了!!
8.4.3 移除一个节点 当找到 node.key 的时候还有三种情况 1.无子叶 2.只有右子节点 3.只有左子节点 4.有两个子节点–需要找到右子叶最小的节点,将这个节点提到删除的那个节点去,并删除这个节点。
8.5 更多关于二叉树的知识 平衡二叉树搜索树(AVL):因为上边讨论的方法存在一条边非常深的情况,所以通过平衡二叉树来设置左右两侧子树的高度之差最多为 1.
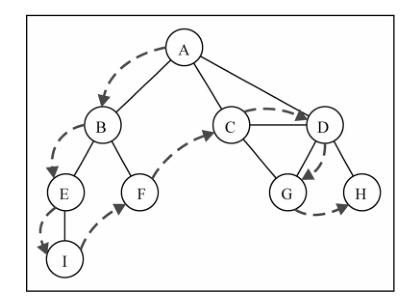
9. 图 图–非线性数据结构
9.1 图的相关术语 边(E):
解决的问题:比如搜索图中的一个特定顶点或搜索一条特定边,寻找图中的一条路径(从一个顶点到另一个顶点),寻找两个顶点之间的最短路径,以及环检测。
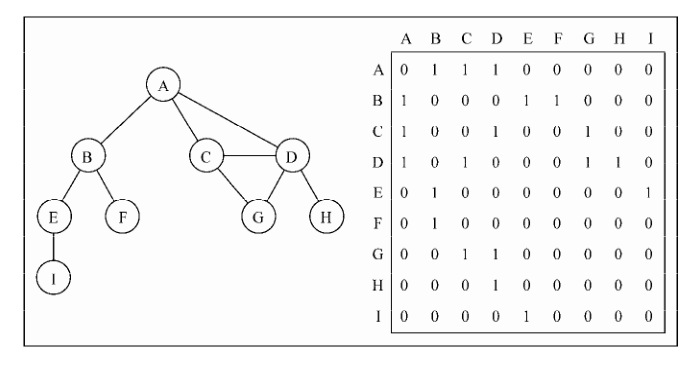
9.2 图的表示 9.2.1 邻接矩阵 如果索引为 i 的节点和索引为 j 的节点相邻,则 array[i][j]=== 1,否则 array[i][j] === 0
缺点: 1.不是强连通的图(稀疏图)如果用邻接矩阵来表示,则矩阵中将会有很多 0,这意味着我们浪费了计算机存储空间 来表示根本不存在的边。 2.图中顶点的数量可能会改变,而 2 维数组不太灵活。
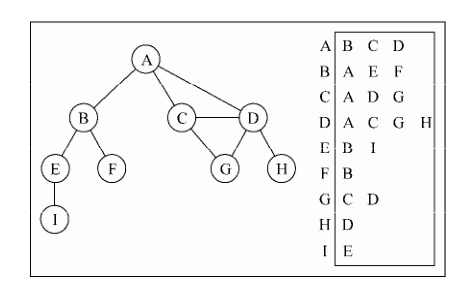
9.2.2 邻接表 可以用列表(数组)、链表,甚至是散列表或是字典来表示相邻顶点列表。(表第一行里的 BCD)
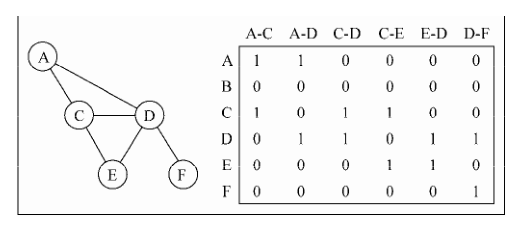
9.2.3 关联矩阵 如果顶点 v 是边 e 的入射点,则 array[v][e] === 1;否则,array[v][e] === 0。
9.3 创建图类 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 function Graph() { var vertices = []; //list var adjList = new Dictionary(); this.addVertex = function(v){ vertices.push(v); adjList.set(v, []); //initialize adjacency list with array as well; }; this.addEdge = function(v, w){ adjList.get(v).push(w); //adjList.get(w).push(v); //commented to run the improved DFS with topological sorting }; this.toString = function(){ var s = ''; for (var i=0; i<vertices.length; i++){ s += vertices[i] + ' -> '; var neighbors = adjList.get(vertices[i]); for (var j=0; j<neighbors.length; j++){ s += neighbors[j] + ' '; } s += '\n'; } return s; }; var initializeColor = function(){ var color = []; for (var i=0; i<vertices.length; i++){ color[vertices[i]] = 'white'; } return color; }; this.bfs = function(v, callback){ var color = initializeColor(), queue = new Queue(); queue.enqueue(v); while (!queue.isEmpty()){ var u = queue.dequeue(), neighbors = adjList.get(u); color[u] = 'grey'; for (var i=0; i<neighbors.length; i++){ var w = neighbors[i]; if (color[w] === 'white'){ color[w] = 'grey'; queue.enqueue(w); } } color[u] = 'black'; if (callback) { callback(u); } } }; this.dfs = function(callback){ var color = initializeColor(); for (var i=0; i<vertices.length; i++){ if (color[vertices[i]] === 'white'){ dfsVisit(vertices[i], color, callback); } } }; var dfsVisit = function(u, color, callback){ color[u] = 'grey'; if (callback) { callback(u); } console.log('Discovered ' + u); var neighbors = adjList.get(u); for (var i=0; i<neighbors.length; i++){ var w = neighbors[i]; if (color[w] === 'white'){ dfsVisit(w, color, callback); } } color[u] = 'black'; console.log('explored ' + u); }; this.BFS = function(v){ var color = initializeColor(), queue = new Queue(), d = [], pred = []; queue.enqueue(v); for (var i=0; i<vertices.length; i++){ d[vertices[i]] = 0; pred[vertices[i]] = null; } while (!queue.isEmpty()){ var u = queue.dequeue(), neighbors = adjList.get(u); color[u] = 'grey'; for (i=0; i<neighbors.length; i++){ var w = neighbors[i]; if (color[w] === 'white'){ color[w] = 'grey'; d[w] = d[u] + 1; pred[w] = u; queue.enqueue(w); } } color[u] = 'black'; } return { distances: d, predecessors: pred }; }; var time = 0; this.DFS = function(){ var color = initializeColor(), d = [], f = [], p = []; time = 0; for (var i=0; i<vertices.length; i++){ f[vertices[i]] = 0; d[vertices[i]] = 0; p[vertices[i]] = null; } for (i=0; i<vertices.length; i++){ if (color[vertices[i]] === 'white'){ DFSVisit(vertices[i], color, d, f, p); } } return { discovery: d, finished: f, predecessors: p }; }; var DFSVisit = function(u, color, d, f, p){ console.log('discovered ' + u); color[u] = 'grey'; d[u] = ++time; var neighbors = adjList.get(u); for (var i=0; i<neighbors.length; i++){ var w = neighbors[i]; if (color[w] === 'white'){ p[w] = u; DFSVisit(w,color, d, f, p); } } color[u] = 'black'; f[u] = ++time; console.log('explored ' + u); }; }
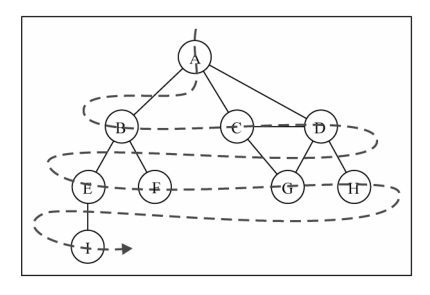
9.4 图的遍历 分为广度优先搜索(BFS)和深度优先搜索(DFS)
9.4.1 广度优先搜索 数据结构—栈
步骤:
9.4.1.1 使用 BFS 寻找最短路径–从一个点到另外其他点所需要的路径 只是给原式添加两个参数:
9.4.1.2 深入学习最短路径 本章中的图不是加权图。如果要计算加权图中的最短路径(例如,城市 A 和城市 B 之间的最
9.4.2 深度优先搜索 数据结构—队列
9.4.2.1 探索深度优先算法 9.4.2.2 拓扑排序-使用深度优先搜索 10. 排序和搜索算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 function ArrayList(){ var array = []; this.insert = function(item){ array.push(item); }; var swap = function(index1, index2){ var aux = array[index1]; array[index1] = array[index2]; array[index2] = aux; }; this.toString= function(){ return array.join(); }; //冒泡排序 this.bubbleSort = function(){ var length = array.length; for (var i=0; i<length; i++){ console.log('--- '); for (var j=0; j<length-1; j++ ){ console.log('compare ' + array[j] + ' with ' + array[j+1]); if (array[j] > array[j+1]){ console.log('swap ' + array[j] + ' with ' + array[j+1]); swap(j, j+1); } } } }; //改进后的冒泡算法 this.modifiedBubbleSort = function(){ var length = array.length; for (var i=0; i<length; i++){ console.log('--- '); for (var j=0; j<length-1-i; j++ ){ //改了这里--已经比较后,放在最后的就不需要再比较一次了 console.log('compare ' + array[j] + ' with ' + array[j+1]); if (array[j] > array[j+1]){ console.log('swap ' + array[j] + ' with ' + array[j+1]); swap(j, j+1); } } } }; //选择排序 --选择排序大致的思路是找到数据结构中的最小值并将其放置在第一位,接着找到第二小的值并将其放在第二位,以此类推。 this.selectionSort = function(){ var length = array.length, indexMin; for (var i=0; i<length-1; i++){ indexMin = i; console.log('index ' + array[i]); for (var j=i; j<length; j++){ if(array[indexMin]>array[j]){ console.log('new index min ' + array[j]); indexMin = j; } } if (i !== indexMin){ console.log('swap ' + array[i] + ' with ' + array[indexMin]); swap(i, indexMin); } } }; //插入排序 --插入排序每次排一个数组项,以此方式构建最后的排序数组。假定第一项已经排序了,接着,它和第二项进行比较,第二项是应该待在原位还是插到第一项之前呢?这样,头两项就已正确排序,接着和第三项比较(它是该插入到第一、第二还是第三的位置呢?),以此类推。 this.insertionSort = function(){ var length = array.length, j, temp; for (var i=1; i<length; i++){ j = i; temp = array[i]; console.log('to be inserted ' + temp); while (j>0 && array[j-1] > temp){ console.log('shift ' + array[j-1]); array[j] = array[j-1]; j--; } console.log('insert ' + temp); array[j] = temp; } }; //归并排序 --归并排序是第一个可以被实际使用的排序算法。你在本书中学到的前三个排序算法性能不好,但归并排序性能不错,其复杂度为O(nlog n )。 //归并排序是一种分治算法。其思想是将原始数组切分成较小的数组,直到每个小数组只有一个位置,接着将小数组归并成较大的数组,直到最后只有一个排序完毕的大数组。 this.mergeSort = function(){ array = mergeSortRec(array); }; var mergeSortRec = function(array){ var length = array.length; if(length === 1) { console.log(array); return array; } var mid = Math.floor(length / 2), left = array.slice(0, mid), right = array.slice(mid, length); return merge(mergeSortRec(left), mergeSortRec(right)); }; var merge = function(left, right){ var result = [], il = 0, ir = 0; while(il < left.length && ir < right.length) { if(left[il] < right[ir]) { result.push(left[il++]); } else{ result.push(right[ir++]); } } while (il < left.length){ result.push(left[il++]); } while (ir < right.length){ result.push(right[ir++]); } console.log(result); return result; }; //快速排序 --快速排序也许是最常用的排序算法了。它的复杂度为O(nlog n ),且它的性能通常比其他的复杂度为O(nlog n )的排序算法要好。 //和归并排序一样,快速排序也使用分治的方法,将原始数组分为较小的数组(但它没有像归并排序那样将它们分割开)。 this.quickSort = function(){ quick(array, 0, array.length - 1); }; var partition = function(array, left, right) { var pivot = array[Math.floor((right + left) / 2)], i = left, j = right; console.log('pivot is ' + pivot + '; left is ' + left + '; right is ' + right); while (i <= j) { while (array[i] < pivot) { i++; console.log('i = ' + i); } while (array[j] > pivot) { j--; console.log('j = ' + j); } if (i <= j) { console.log('swap ' + array[i] + ' with ' + array[j]); swapQuickStort(array, i, j); i++; j--; } } return i; }; var swapQuickStort = function(array, index1, index2){ var aux = array[index1]; array[index1] = array[index2]; array[index2] = aux; }; var quick = function(array, left, right){ var index; if (array.length > 1) { index = partition(array, left, right); if (left < index - 1) { quick(array, left, index - 1); } if (index < right) { quick(array, index, right); } } return array; }; //顺序搜索 --就是判断相等 this.sequentialSearch = function(item){ for (var i=0; i<array.length; i++){ if (item === array[i]){ return i; } } return -1; }; this.findMaxValue = function(){ var max = array[0]; for (var i=1; i<array.length; i++){ if (max < array[i]){ max = array[i]; } } return max; }; this.findMinValue = function(){ var min = array[0]; for (var i=1; i<array.length; i++){ if (min > array[i]){ min = array[i]; } } return min; }; //二分搜索 --不大于不小于则一定相等 this.binarySearch = function(item){ this.quickSort(); var low = 0, high = array.length - 1, mid, element; while (low <= high){ mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2); element = array[mid]; console.log('mid element is ' + element); if (element < item) { low = mid + 1; console.log('low is ' + low); } else if (element > item) { high = mid - 1; console.log('high is ' + high); } else { console.log('found it'); return mid; } } return -1; }; }
11. 算法补充知识 11.1 递归 一定要有边界条件 跳转指令 而不是子程序调用 时间和次数 控制何时溢出错误
11.1.2 斐波那契数列 定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 //递归 function fibonacci(num){ if (num === 1 || num === 2){ return 1; } if (num > 2){ return fibonacci(num - 1) + fibonacci(num - 2); } } //循环 function fib(num){ var n1 = 1, n2 = 1, n = 1; for (var i = 3; i<=num; i++){ n = n1 + n2; n1 = n2; n2 = n; } return n; } console.log(fibonacci(6)); console.log(fib(6));
ES6 用了尾调用优化,所以递归并不会更慢
11.2 动态规划 比较难-没搞懂
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 function MinCoinChange(coins){ var coins = coins; var cache = {}; this.makeChange = function(amount) { var me = this; if (!amount) { return []; } if (cache[amount]) { return cache[amount]; } var min = [], newMin, newAmount; for (var i=0; i<coins.length; i++){ var coin = coins[i]; newAmount = amount - coin; if (newAmount >= 0){ newMin = me.makeChange(newAmount); } if ( newAmount >= 0 && (newMin.length < min.length || !min.length) && (newMin.length || !newAmount) ){ min = [coin].concat(newMin); console.log('new Min ' + min + ' for ' + amount); } } return (cache[amount] = min); }; } var minCoinChange = new MinCoinChange([1, 5, 16, 28]); console.log(minCoinChange.makeChange(32));
11.3 贪心算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 function MinCoinChange(coins){ var coins = coins; var cache = {}; this.makeChange = function(amount) { var change = [], total = 0; for (var i=coins.length; i>=0; i--){ var coin = coins[i]; while (total + coin <= amount) { change.push(coin); total += coin; } } return change; }; } var minCoinChange = new MinCoinChange([1, 5, 10, 25]); console.log(minCoinChange.makeChange(36)); var minCoinChange2 = new MinCoinChange([1, 3, 4]); console.log(minCoinChange2.makeChange(6));
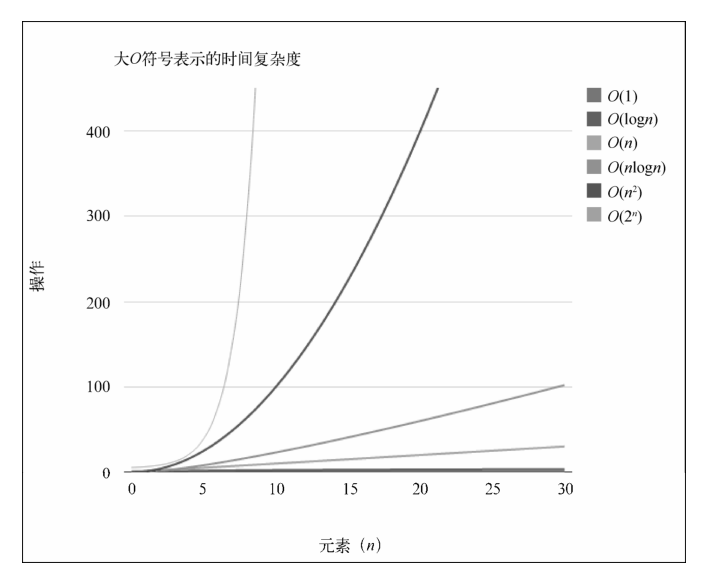
11.4 大 O 表示法
11.4.1 理解大 O 表示法 当讨论大 O 表示法时,一般考虑的是 CPU(时间)占用。
11.4.2 时间复杂度的比较
遇到的类算法公式 计算两个数字之间最大的公共除数(gcd) harmony 1 2 const gcd = (x, y ) => (!y ? x : gcd(y, x % y));
解读:其实就是相当于找到余数的公共除数
斐波那契数列 // 递归特别慢,采用循环
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 function fib (n ) let array = new Array (n + 1 ).fill(null ); array[0 ] = 0 ; array[1 ] = 1 ; for (let i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { array[i] = array[i - 1 ] + array[i - 2 ]; } return array[n]; } fib(10 );
排序 冒泡算法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function checkArray (array ) if (!array) return ; } function swap (array, left, right ) let rightValue = array[right]; array[right] = array[left]; array[left] = rightValue; } function bubble (array ) checkArray(array); for (let i = array.length - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { for (let j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (array[j] > array[j + 1 ]) swap(array, j, j + 1 ); } } return array; }
快排 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 var quickSort = function (arr ) if (arr.length <= 1 ) { return arr; } var pivotIndex = Math .floor(arr.length / 2 ); var pivot = arr.splice(pivotIndex, 1 )[0 ]; var left = []; var right = []; for (var i = 0 ; i < arr.length; i++) { if (arr[i] < pivot) { left.push(arr[i]); } else { right.push(arr[i]); } } return quickSort(left).concat([pivot], quickSort(right)); };
归并排序 核心代码部分:利用双指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 function Merger (a, b ) var n = a && a.length; var m = b && b.length; var c = []; var i = 0 , j = 0 ; while (i < n && j < m) { if (a[i] < b[j]) c.push(a[i]); i++ else c.push(b[j]); j++ } while (i < n) c.push(a[i]); i++ while (j < m) c.push(b[j]); j++ console .log("将数组" ,a,'和' ,b,'合并为' ,c) return c; }
动态规划总结 动态规划笔试题
子序列和子串 例如:一个字符串 awbcdewgh
遍历二维数组 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 var d_arr = new Array ();for (let i = 0 ; i < 4 ; i++) { d_arr[i] = new Array (); for (let j = 0 ; j < 4 ; j++) { d_arr[i][j] = 0 ; } } console .log(d_arr);let arr = new Array (5 ).fill(0 ).map((v, index ) => { return new Array (7 ).fill(0 ); }); arr = new Array (5 ).fill(new Array (7 ));
最长公共子序列
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 function LCS (str1, str2 ) var m = str1.length; var n = str2.length; var dp = [new Array (n + 1 ).fill(0 )]; for (var i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { dp[i] = [0 ]; for (var j = 1 ; j <= n; j++) { if (str1[i - 1 ] === str2[j - 1 ]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math .max(dp[i - 1 ][j], dp[i][j - 1 ]); } } } return dp[m][n]; } let s1 = [3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 0 ];let s2 = [1 , 2 , 4 , 6 , 3 , 7 , 9 ];function LCS (s1, s2 ) var sl1 = s1.length; var sl2 = s2.length; var dp = new Array (sl1 + 1 ).fill(0 ).map(item => return new Array (sl2 + 1 ).fill(0 ); }); for (var i = 1 ; i <= sl1; i++) { for (var j = 1 ; j <= sl2; j++) { if (s1[i - 1 ] === s2[j - 1 ]) { dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ] + 1 ; } else { dp[i][j] = Math .max(dp[i][j - 1 ], dp[i - 1 ][j]); } } } console .log(dp, "dp" ); } let arr1 = ["B" , "D" , "C" , "A" , "B" , "A" ];let arr2 = ["A" , "B" , "C" , "B" , "D" , "A" , "B" ];function Fun (s1, s2 ) let twoArray = new Array (s1.length + 1 ).fill(0 ).map(item => return new Array (s2.length + 1 ).fill(0 ); }); twoArray[0 ][0 ] = 0 ; for (let index = 0 ; index < s1.length; index++) { twoArray[index][0 ] = 0 ; for (let index2 = 0 ; index2 < s2.length; index2++) { twoArray[0 ][index2] = 0 ; if (s1[index] === s2[index2]) { twoArray[index + 1 ][index2 + 1 ] = twoArray[index][index2] + 1 ; console .log(printFun(twoArray, s1, s2, index + 1 , index2 + 1 )); } else { twoArray[index + 1 ][index2 + 1 ] = Math .max( twoArray[index][index2 + 1 ], twoArray[index + 1 ][index2] ); } } } console .log(twoArray); } function printFun (twoArray, s1, s2, index, index2 ) if (index == 0 || index2 == 0 ) { return "" ; } if (s1[index - 1 ] === s2[index2 - 1 ]) { return printFun(twoArray, s1, s2, index - 1 , index2 - 1 ) + s1[index - 1 ]; } if (twoArray[index][index2 - 1 ] > twoArray[index - 1 ][index2]) { return printFun(twoArray, s1, s2, index, index2 - 1 ); } else { return printFun(twoArray, s1, s2, index - 1 , index2); } } Fun(arr1, arr2);
参考文献
最长递增子序列 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 function lis (n ) if (n.length === 0 ) return 0 ; let array = new Array (n.length).fill(1 ); for (let i = 1 ; i < n.length; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (n[i] > n[j]) { array[i] = Math .max(array[i], 1 + array[j]); } } } console .log(array); let res = 1 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < array.length; i++) { res = Math .max(res, array[i]); } return res; } lis([3 , 5 , 2 , 6 , 9 , 1 , 3 , 4 ]); var s1 = [3 , 5 , 2 , 6 , 9 , 1 , 3 , 4 ];function fun (s1 ) var countArr = new Array (s1.length).fill(1 ); for (var i = 1 ; i < s1.length; i++) { for (var j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { if (s1[i] > s1[j]) { countArr[i] = Math .max(countArr[i], 1 + countArr[j]); } } } console .log(countArr); } fun(s1);
方法二:
1 2 [3 , 5 , 2 , 6 , 9 , 1 , 3 , 4 ].sort();
01 背包问题 用途:价值总和最大
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 function knapsack (weights, values, W ) var n = weights.length - 1 ; var f = [[]]; for (var j = 0 ; j <= W; j++) { if (j < weights[0 ]) { f[0 ][j] = 0 ; } else { f[0 ][j] = values[0 ]; } } for (var j = 0 ; j <= W; j++) { for (var i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { if (!f[i]) { f[i] = []; } if (j < weights[i]) { f[i][j] = f[i - 1 ][j]; } else { f[i][j] = Math .max(f[i - 1 ][j], f[i - 1 ][j - weights[i]] + values[i]); } } } return f[n][W]; } var a = knapsack([2 , 2 , 6 , 5 , 4 ], [6 , 3 , 5 , 4 , 6 ], 10 );console .log(a);let weight = [2 , 2 , 6 , 5 , 4 ];let values = [6 , 3 , 5 , 4 , 6 ];let W = 10 ;function fun (weight, values, W ) let TDA = new Array (W + 1 ).fill(0 ).map(item => return new Array (weight.length).fill(0 ); }); for (var i = 0 ; i <= W; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j < weight.length; j++) { if (i >= weight[j]) { if (j > 0 ) { let push = values[j] + TDA[i - weight[j]][j - 1 ]; let noPush = TDA[i][j - 1 ]; TDA[i][j] = Math .max(push, noPush); } else { TDA[i][j] = values[0 ]; } } else { if (j > 0 ) { TDA[i][j] = TDA[i][j - 1 ]; } else { TDA[i][j] = 0 ; } } } } console .log(TDA); } fun(weight, values, W); function knapsack (w, v, C ) let length = w.length; if (length === 0 ) return 0 ; let array = new Array (length).fill(new Array (C + 1 ).fill(null )); for (let i = 0 ; i <= C; i++) { array[0 ][i] = i >= w[0 ] ? v[0 ] : 0 ; } for (let i = 1 ; i < length; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j <= C; j++) { array[i][j] = array[i - 1 ][j]; if (j >= w[i]) { array[i][j] = Math .max(array[i][j], v[i] + array[i - 1 ][j - w[i]]); } } } return array[length - 1 ][C]; } var money = [1 , 2 , 5 , 10 , 20 , 50 , 100 ];function fun (n ) let arr = new Array (n + 1 ).fill(0 ).map(item => return new Array (money.length).fill(0 ); }); for (var i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { if (i < money[0 ]) { arr[i][0 ] = 0 ; } else { arr[i][0 ] = 1 ; } } for (var i = 0 ; i <= n; i++) { for (var j = 1 ; j < money.length; j++) { if (i >= money[j]) { arr[i][j] = Math .max( arr[i][j - 1 ], arr[i - money[j]][j - 1 ] + money[j] ); } else { arr[i][j] = arr[i][j - 1 ]; } } } console .log(arr[100 ], "100" ); } fun(110 ); for (var i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (var j = 0 ; j <= W; j++) { f[i][j] = Math .max(f[i - 1 ][j], f[i - 1 ][j - weights[i]] + values[i]); } } for (var i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (var j = 0 ; j <= W; j++) { for (var k = 0 ; k < j / weights[i]; k++) { f[i][j] = Math .max( f[i - 1 ][j], f[i - 1 ][j - k * weights[i]] + k * values[i] ); } } } for (let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { f[i] = []; for (let j = 0 ; j <= W; j++) { if (j < weights[i]) { f[i][j] = f[i - 1 ][j]; } else { f[i][j] = Math .max(f[i - 1 ][j], f[i][j - weights[i]] + values[i]); } } }
参考文献 动态规划
树结构 树的数据结构 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 let a = { value: '1' left: { value: '2' , left:{}, right:{} }, right:{ value: '3' , left:{}, right:{} } }
树的添加,查找和删除节点 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 class Node constructor (data, left, right) { this .data = data; this .left = left; this .right = right; } } class Tree constructor () { this .root = null ; this .deepDataList = []; this .breadthDataList = []; this .breadthNodeList = []; this .breadthCount = 0 ; } insert(data) { let newNode = new Node(data, null , null ); if (!this .root) { return (this .root = newNode); } let currentNode = this .root; while (1 ) { if (data < currentNode.data) { if (currentNode.left) { currentNode = currentNode.left; } else { currentNode.left = newNode; break ; } } else { if (currentNode.right) { currentNode = currentNode.right; } else { currentNode.right = newNode; break ; } } } } preTraversal(node) { if (!node) return ; console .log(node.data, "pre" ); this .preTraversal(node.left); this .preTraversal(node.right); } midTraversal(node) { if (!node) return ; this .midTraversal(node.left); console .log(node.data, "mid" ); this .midTraversal(node.right); } backTraversal(node) { if (!node) return ; this .backTraversal(node.left); this .backTraversal(node.right); console .log(node.data, "back" ); } deepTraversal(node) { if (node) { this .deepDataList.push(node.data); this .deepTraversal(node.left); this .deepTraversal(node.right); } } breadthTraversal(root) { if (root) { this .breadthNodeList[this .breadthCount] = root; } let node = this .breadthNodeList[this .breadthCount]; if (node) { this .breadthDataList.push(node.data); this .breadthNodeList.push(node.left); this .breadthNodeList.push(node.right); this .breadthCount++; this .breadthTraversal(); } } var levelOrder = function (root ) if (!root) { return []; } const data = []; const queue = [root]; while (queue.length) { const first = queue.shift(); data.push(first.val); first.left && queue.push(first.left); first.right && queue.push(first.right); } return data; }; maxDepth(node) { if (!node) return 0 ; return Math .max(this .maxDepth(node.left), this .maxDepth(node.right)) + 1 ; } find(searchNode, node) { if (searchNode.data == node.data) { return node.data; } find(node.left); find(node.right); } } let tree = new Tree();tree.insert(6 ); tree.insert(4 ); tree.insert(3 ); tree.insert(5 ); tree.insert(8 ); tree.insert(7 ); tree.insert(9 ); console .log(tree.maxDepth(tree.root));class BinarySearchTree constructor () { this .root = null ; } insert(data) { let n = new Node(data, null , null ); if (!this .root) { return (this .root = n); } let currentNode = this .root; let parent = null ; while (1 ) { parent = currentNode; if (data < currentNode.data) { currentNode = currentNode.left; if (currentNode === null ) { parent.left = n; break ; } } else { currentNode = currentNode.right; if (currentNode === null ) { parent.right = n; break ; } } } } remove(data) { this .root = this .removeNode(this .root, data); } removeNode(node, data) { if (node == null ) { return null ; } if (data == node.data) { if (node.left == null && node.right == null ) { return null ; } if (node.left == null ) { return node.right; } if (node.right == null ) { return node.left; } let getSmallest = function (node ) if (node.left === null && node.right == null ) { return node; } if (node.left != null ) { return node.left; } if (node.right !== null ) { return getSmallest(node.right); } }; let temNode = getSmallest(node.right); node.data = temNode.data; node.right = this .removeNode(temNode.right, temNode.data); return node; } else if (data < node.data) { node.left = this .removeNode(node.left, data); return node; } else { node.right = this .removeNode(node.right, data); return node; } } find(data) { var current = this .root; while (current != null ) { if (data == current.data) { break ; } if (data < current.data) { current = current.left; } else { current = current.right; } } return current.data; } } module .exports = BinarySearchTree;var buildTree = function (preorder, inorder ) var result = null ; if (preorder.length > 1 ){ var index = inorder.indexOf(preorder[0 ]); result = { val: preorder[0 ], left: buildTree(preorder.slice(1 , index + 1 ), inorder.slice(0 , index)), right: buildTree(preorder.slice(index + 1 ), inorder.slice(index + 1 )) } }else if (preorder.length == 1 ){ result = { val: preorder[0 ], left: null , right: null } } return result; }; console .log(buildTree([3 ,9 ,20 ,15 ,7 ], [9 ,3 ,15 ,20 ,7 ]))
树的深度 1 2 3 4 var maxDepth = function (root ) if (!root) return 0 ; return Math .max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1 ; };
二维数组的全排列组合 用途:一共有多少种方法
// 核心思想就是 从 0 开始, 一点一点+1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 function printArr (arr, n, res ) for (var i = 0 ; i < arr[i].length; i++) { if (n == 0 ) { res = []; } if (n < arr.length) { var _res = res.slice(); _res.push(arr[n][i]); if (n == arr.length - 1 ) { console .log(_res); } else { printArr(arr, n + 1 , _res); } } } } var arr = [ [1 , 2 ], [3 , 4 ], [5 , 6 ] ]; printArr(arr, 0 ); var arr = [ [1 , 2 ], [3 , 4 ], [5 , 6 ] ]; function printArr (arr, n, res ) if (n == 0 ) res = []; var i = 0 ; while (i < arr[n].length) { var newRes = res.slice(); newRes.push(arr[n][i]); if (n == arr.length - 1 ) { console .log(newRes); } else { var newN = n + 1 ; printArr(arr, newN, newRes); } i++; } } printArr(arr, 0 );
打印青蛙跳台阶的所有方式 注意 不是求方式的个数,而是打印每种情况台阶数为 10,每次跳 1 次或两次
可以拆开为[[1,2],[1,2],[1,2]] 这样,控制总数为 10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function step (n, res ) if (n == 0 ) { res = []; } var i = 1 ; while (i < 3 ) { if (n + i <= 10 ) { var _res = res.slice(); _res.push(i); if (n + i == 10 ) { console .log(_res); } else { step(n + i, _res); } } i++; } } step(0 );
变种: [10,20,50,100] 随便取最后得 1000
计算数位之和 例如:78 就是 7+8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function bitSum (n ) let res = 0 ; while (n) { res = res + (n % 10 ); n = Math .floor(n / 10 ); } return res; }